Hpw to Read Data From a File in Kafka Streams
Editor's note: This article was updated on 3 March 2022 to include information nearly Apache Kafka version 3.1.0, besides as an overview of KRaft.
A study from the McKinsey Global Institute reveals that data-driven organizations are 23 times more likely to learn customers, six times as probable to retain customers, and xix times as likely to be profitable.
In an intelligible and usable format, data can help drive business needs. Yet, large tech companies collect user data in raw form. And so, the challenge is to process and, if necessary, transform or clean the information to make sense of it.
Basic data streaming applications move data from a source bucket to a destination saucepan. More complex applications that involve streams perform some magic on the wing, similar altering the structure of the output data or enriching it with new attributes or fields.
In this article, we'll review Apache Kafka's key concepts and terms and will demonstrate how to use Kafka to build a minimal real-time data streaming awarding.
Our tutorial volition follow these steps:
- Installing Kafka locally
- Configuring the Kafka Cluster
- Bootstrapping the application and installing dependencies
- Creating topics with Kafka
- Producing content with Kafka
- Consuming content with Kafka
- Running the real-time information streaming app
Prerequisites
To follow forth with this tutorial, the following prerequisites are required:
- The latest versions of Node.js and npm installed
- The latest Java version (JVM) installed
- Kafka installed North.B., in this tutorial, we'll review installing Kafka locally
- A basic understanding of writing Node.js applications
Batch processing
Information transformation and/or enrichment is generally handled as it is consumed from an input topic to be used by some other awarding or an output topic. This is a very common scenario in data engineering, as there is ever a need to clean up, transform, aggregate, or even reprocess usually raw and temporarily stored data in a Kafka topic to make it suit to a detail standard or format.
Background and key concepts
According to its website, Kafka is an open up-source, highly distributed streaming platform. Built by the engineers at LinkedIn (now part of the Apache software foundation), Kafka is a reliable, resilient, and scalable system that supports streaming events/applications. It is horizontally scalable, fault-tolerant by default, and offers loftier speed. Kafka has a diversity of use cases, one of which is to build data pipelines or applications that handle streaming events and/or processing of batch data in existent time. At the time of writing, the latest Kafka version is 3.1.0.
Here are some of Kafka's basic concepts and terms:
- Topic: Kafka topics are a grouping of partitions or groups beyond multiple Kafka brokers. The topic acts as an intermittent storage mechanism for streamed information in the cluster. For each Kafka topic, we tin choose to set the replication factor and other parameters similar the number of partitions
- Producers, Consumers, and Clusters: Producers are clients that produce or write data to Kafka brokers or Kafka topics to be more precise. Consumers, on the other manus, read information or — as the name implies — consume data from Kafka topics or Kafka brokers. A Cluster is just a group of brokers or servers that powers a current Kafka instance
- KRaft: The recent release of Kafka introduced Kafka Raft metadata way (KRaft) which simplifies Kafka's compages by removing its dependency on ZooKeeper. Before the introduction of KRaft, ZooKeeper was used to keep track of Kafka's cluster state and control the synchronization and configuration of Kafka brokers or servers. Every bit a second system, ZooKeeper added to the complexity of Kafka's compages. Nether Zookeeper, metadata was stored outside of Kafka in a Zookeeper cluster. Nether KRaft, all metadata is stored and managed inside Kafka

For more detailed information on all these of import concepts, bank check out the Apache Kafka documentation.
In this article, y'all'll larn how to use Apache Kafka to build a data pipeline to motion batch information. As a demo, we'll simulate a large JSON data shop generated at a source. Then, we'll write a produced script that writes this JSON data from a source at, say, indicate A to a particular topic on our local broker/cluster Kafka setup. Finally, we'll write a consumer script that consumes the stored data from the specified Kafka topic.
Installing Kafka
To install Kafka, download the latest version here and extract it with the following commands:
tar -xzf kafka_2.13-3.1.0.tgz cd kafka_2.13-3.1.0
The tar command extracts the downloaded Kafka binary. The Kafka binaries tin can be downloaded on any path we desire.
Next, navigate to the directory where Kafka is installed and run the ls command. And then, cd into the bin directory and run ls again:
bin folder.If nosotros go a level up with the cd .. command and run ls, nosotros'll notice a config folder.
The config binder contains a server.properties file that we'll use to configure the Kafka server and include whatever desired changes or configurations.
Now, run the following commands:
cd .. ls cd config ls nano server.properties
config directory.KRaft's controllers are used to store all metadata inside Kafka. The pb KRaft controller is responsible for providing the latest state for the Kafka brokers. The other KRaft controllers are always on standby in instance the lead controller ever fails.
At present, we'll start writing the configurations for our Kafka server to set up the Kafka cluster.
Configuring the Kafka cluster
Here, we'll set up our Kafka cluster, which volition consist of the Kafka brokers (servers) that are running. All configurations will exist done in the config directory and in the server.properties file.
First, nosotros'll ensure that we're yet in the config directory. Then, we'll run these commands:
cd kraft ls
Next, re-create the server.properties into a new file called server1.backdrop and start editing the file using the following commands:
cp server.backdrop server1.properties nano server1.backdrop
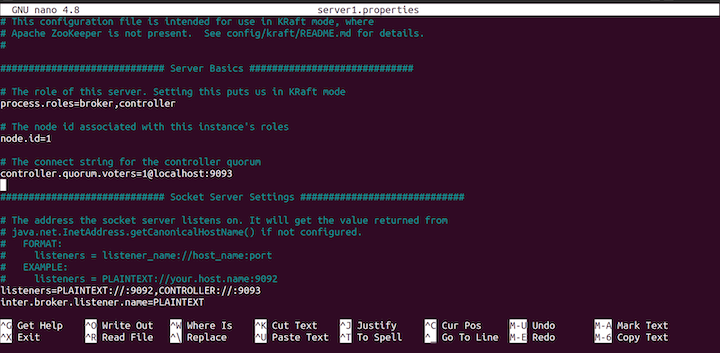
config file.In this code, process.roles is set to both broker and controller. This means that the same server will act as both the banker and the controller.
We'll have three servers with id: ane, 2, and 3 and iii controllers running on port localhost:19092, localhost:19093, and locahost:19094. The post-obit Kafka brokers will be running in the port: 9092, 9093, 9094.
Now, with the KRaft config file open, set up the controller.qorum.voters to the following:
[email protected]:19092,[email protected]:19093,[email protected]:19094
Next, curl downward and set the listeners like so:
listeners=PLAINTEXT://:9092,CONTROLLER://:19092
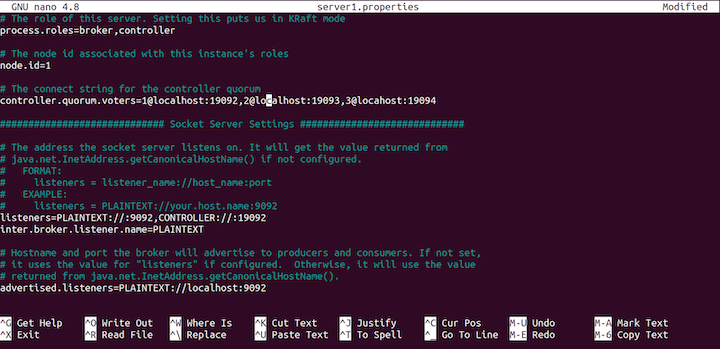
config file.We'll need to alter the destination of the log files, as follows:
log.dirs=/tmp/server1/kraft-combined-logs
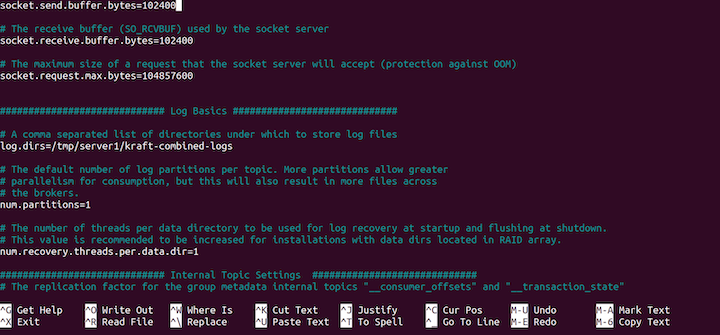
Finally, type CTRL 10 and yes at the prompt to save our configurations.
Now, we've successfully created a re-create of one server and configured the copy. Next, nosotros'll create two additional copies of the server from the server1.properties. Run the following commands:
cp server1.properties server2.properties cp server1.properties server3.properties ls
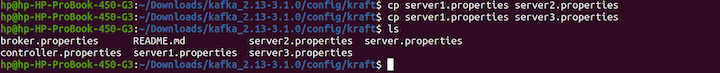
Next, you lot'll add configurations to server2.properties by running this command:
nano server2.properties
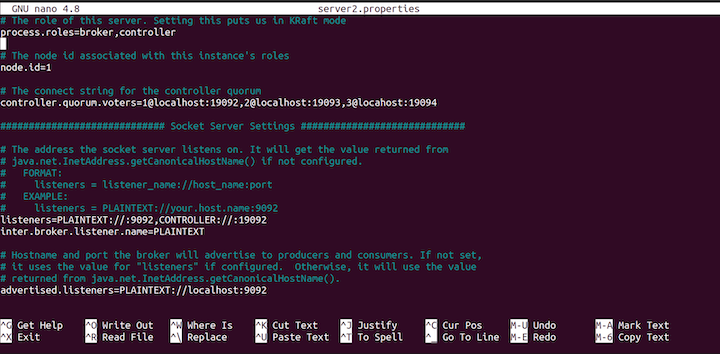
server2.properties file.Change the node.id to 2:
node.id=2
And then, change the listeners, equally follows:
listeners=PLAINTEXT://:9093,CONTROLLER://:19093
Modify the advertised.listeners, as well:
advertised.listeners=PLAINTEXT://localhost:9093
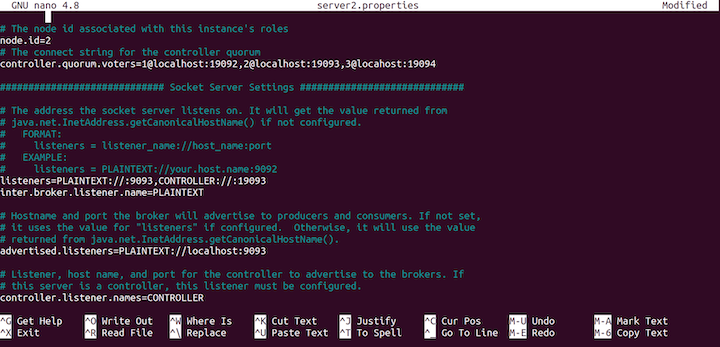
server2.properties.Next, change the log directory log.dirs:
log.dirs=/tmp/server2/kraft-combined-logs
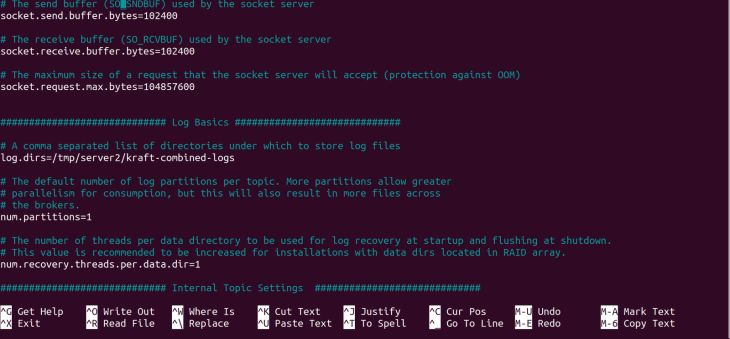
server2.backdrop.That's all the configuration for the server2.backdrop server. Type CTRL 10 and yes at the prompt to salve our configurations.
Next, nosotros'll configure the third server, server3.properties.
Run the following command to start configuring the file:
nano server3.backdrop
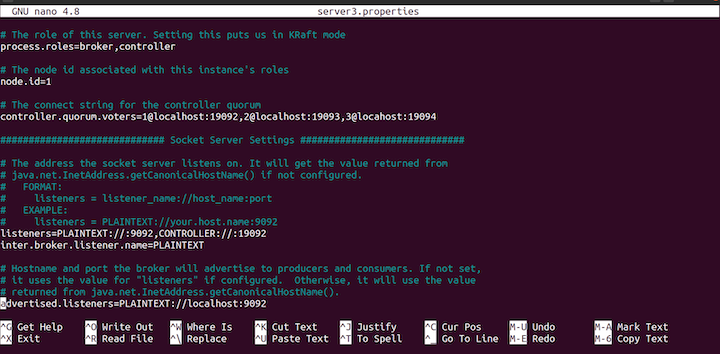
server3.backdrop file.Update the node.id to 3 as follows:
node.id=3
So, change the listeners, like and so:
listeners=PLAINTEXT://:9094,CONTROLLER://:19094
Change the advertised.listeners to the post-obit:
advertised.listeners=PLAINTEXT://localhost:9094
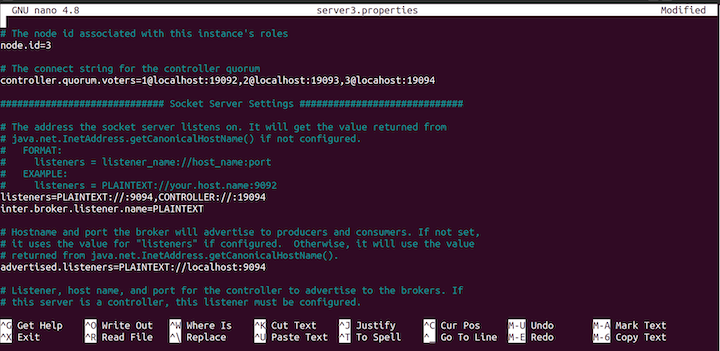
server3.properties file.Change the log directory, log.dirs, with the following command:
log.dirs=/tmp/server3/kraft-combined-logs
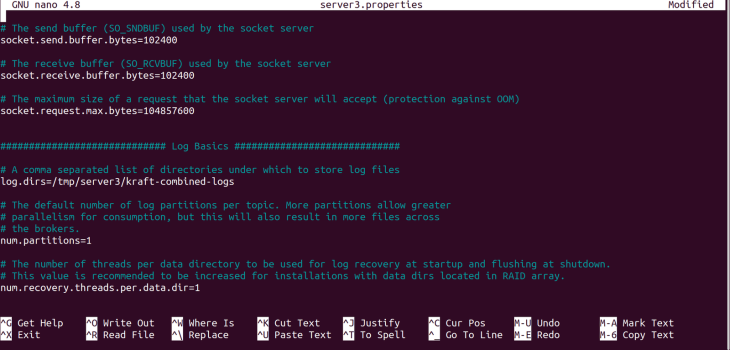
server3.properties.Next, utilise the post-obit command to create an ID for our cluster:
cd .. cd .. ./bin/kafka-storage.sh random-uuid
Once you run the commands, a unique ID will exist logged out. Ensure y'all copy the ID, every bit we'll utilise information technology afterwards:

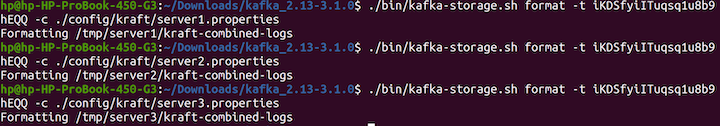
Next, we'll format the location of the log directories to allow Kafka to shop the logs:
./bin/kafka-storage.sh format -t iKDSfyiITuqsq1u8b9hEQQ -c ./config/kraft/server1.properties ./bin/kafka-storage.sh format -t iKDSfyiITuqsq1u8b9hEQQ -c ./config/kraft/server2.properties ./bin/kafka-storage.sh format -t iKDSfyiITuqsq1u8b9hEQQ -c ./config/kraft/server3.backdrop
Here's the output:
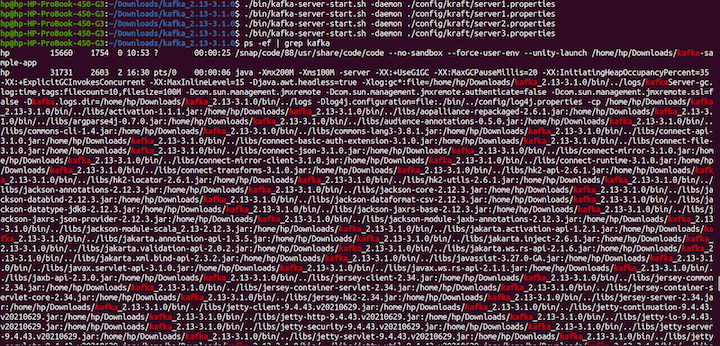
At this bespeak, our severs are not running. Beginning the servers with the post-obit command:
export KAFKA_HEAP_OPTS="-Xmx200M -Xms100M" ./bin/kafka-server-start.sh -daemon ./config/kraft/server1.properties ./bin/kafka-server-start.sh -daemon ./config/kraft/server2.properties ./bin/kafka-server-showtime.sh -daemon ./config/kraft/server3.backdrop ps -ef | grep kafka
Now that nosotros know how to configure the Kafka server, information technology is time to learn how to create topics.
Run the following command:
./bin/kafka-topics.sh --create --topic kraft-test --partitions 3 --replication-factor iii --bootstrap-server localhost:9092
In this tutorial, we'll be using the kafka-node client library for Node.js. Kafka has other clients for other programming languages also, so feel free to use Kafka for any language of your choosing. At the time of this writing, KRaft is not product-fix and may only be used in development style. For this tutorial, we will use ZooKeeper.
Bootstrapping the awarding and installing dependencies
Since we're using Node.js in this practise, nosotros'll begin past bootstrapping a basic application with a minimal structure.
To starting time, we'll create a new directory to house the projection and navigate into information technology, like so:
mkdir kafka-sample-app cd kafka-sample-app
Next, we'll create a package.json file past running the npm init command. And then, nosotros'll follow the instructions to ready the projection equally usual.
The package.json file should look like this afterward the project is set up:
{ "name": "kafka-producer_consumer_tutorial", "version": "ane.0.0", "clarification": "Edifice a existent-time data streaming application pipeline with Apache Kafka\"", "principal": "app.js", "scripts": { "test": "echo \"Error: no test specified\" && exit 1", "start": "node producer.js" }, "writer": "Deborah Emeni", "license": "ISC", "dependencies": { "dotenv": "^xvi.0.0", "kafka-node": "^5.0.0" } } We've installed two dependencies that nosotros'll need later. To install the kafka-node client, we run npm install kafka-node on the terminal. The documentation for kafka-node is available on npm. The dotenv packet is used for setting up environment variables for the app.
Nosotros tin can install the parcel by running npm install dotenv.
Now that nosotros're finished installing the dependencies, permit's create all the necessary files as shown in the figure below:
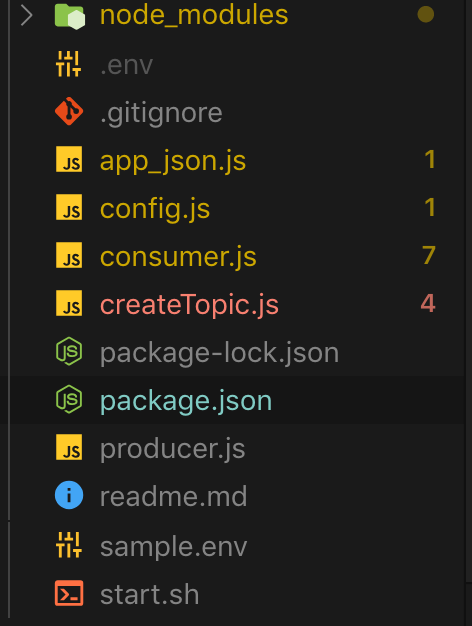
Creating topics
The above figure shows all the necessary files required by the application. Let's take a closer expect at each file to understand what'southward going on.
First, let's manually create a new topic from the concluding with three partitions and replicas with the following control:
./kafka-topics.sh --create --zookeeper --replication-cistron --partitions --topic
In an bodily awarding, we should always update the <ZOOKEEPER_URL:PORT>, <NO_OF_REPLICATIONS>, <NO_OF_PARTITIONS>, and <TOPIC_NAME> with real values. Still, for the purpose of this tutorial, we'll handle that with a script. The code for creating a new topic tin be found in the [createTopic.js] file.
Here's the code:
const kafka = crave('kafka-node'); const config = require('./config'); const client = new kafka.KafkaClient({kafkaHost: config.KafkaHost}); const topicToCreate = [{ topic: config.KafkaTopic, partitions: i, replicationFactor: 1 } ]; client.createTopics(topicToCreate, (error, issue) => { // consequence is an array of whatever errors if a given topic could not exist created panel.log(result, 'topic created successfully'); }); Here, we import the Kafka client and connect to the Kafka setup. Yous'll notice that we never configured a replication gene in our use case. However, this does not mirror a real-life scenario.
In production use cases, we can ready up multiple Kafka brokers based on the volume of data or messages we intend to procedure. Let's see how we can achieve that in the local ready upwardly.
Producing content
Now that we've created a topic, we can produce (or write) data (or content) to the topic. The lawmaking for writing to a topic is institute in the [producer.js] file.
Hither's the code:
const Kafka = require('kafka-node'); const config = require('./config'); const Producer = Kafka.Producer; const client = new Kafka.KafkaClient({kafkaHost: config.KafkaHost}); const producer = new Producer(client, {requireAcks: 0, partitionerType: ii}); const pushDataToKafka =(dataToPush) => { endeavour { let payloadToKafkaTopic = [{topic: config.KafkaTopic, messages: JSON.stringify(dataToPush) }]; panel.log(payloadToKafkaTopic); producer.on('set up', async office() { producer.send(payloadToKafkaTopic, (err, data) => { panel.log('data: ', information); }); producer.on('error', function(err) { // handle error cases here }) }) } catch(mistake) { console.log(fault); } }; const jsonData = require('./app_json.js'); pushDataToKafka(jsonData); Hither, nosotros imported the kafka-node library and ready the customer to receive a connection from the Kafka producer or broker. One time that connection is gear up, nosotros produce data to the specified KafkaTopic. Note that in real-world applications, the client's connection should e'er exist closed once the publish task is complete by calling the client.close() method.
At present, if we run the start script using the ./commencement.sh command, we'll become the data written to our Kafka topic:
npm showtime
Consuming content
To read the topic data (or content), nosotros can use the Consumer script in the [consumer.js] file.
If we run node ./consumer.js, we'll get the following output:
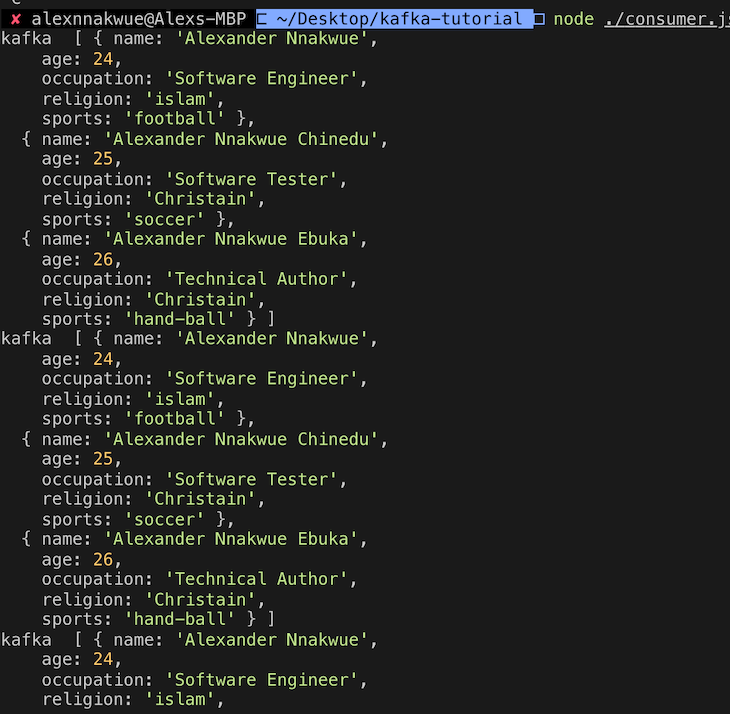
Here'south the code for the consumer.js file:
const kafka = require('kafka-node'); const config = require('./config'); try { const Consumer = kafka.Consumer; const customer = new kafka.KafkaClient({idleConnection: 24 * 60 * 60 * 1000, kafkaHost: config.KafkaHost}); permit consumer = new Consumer( client, [{ topic: config.KafkaTopic, partition: 0 }], { autoCommit: truthful, fetchMaxWaitMs: m, fetchMaxBytes: 1024 * 1024, encoding: 'utf8', // fromOffset: imitation } ); consumer.on('message', async function(message) { console.log( 'kafka ', JSON.parse(message.value) ); }) consumer.on('fault', office(error) { // handle error panel.log('error', fault); }); } catch(error) { // catch fault trace panel.log(error); } Hither, we connect to the Kafka client and swallow data from the predefined Kafka topic.
Running the application
Now that we've completed the setup, we need to start the ZooKeeper server before nosotros tin run the application. This pace is necessary because the Kafka server depends on the ZooKeeper server to run.
To start the ZooKeeper server, run the post-obit command:
bin/zookeeper-server-kickoff.sh config/zookeeper.backdrop
Adjacent, run this command to starting time upwards the Kafka server:
bin/Kafka-server-start.sh config/server.properties
Nosotros can check the number of bachelor Kafka topics in the broker past running this control:
bin/Kafka-topics.sh --listing --zookeeper localhost:2181
We can also swallow data from a Kafka topic by running the console-consumer command:
bin/kafka-console-consumer.sh --bootstrap-server localhost:9092 --topic kafka-case-topic --from-beginning
Additionally, Kafka provides a create script that allows developers to manually create a topic on their cluster:
./kafka-topics.sh --create --zookeeper --replication-gene --partitions --topic
It's important to notation that we need to compulsorily starting time the ZooKeeper and Kafka servers respectively on separate terminal windows before we can create a Kafka topic.
Decision
Kafka tin can deed as a publisher/subscriber blazon of system, used for edifice a read-and-write stream for batch data like to RabbitMQ. It can too be used for building highly resilient, scalable, real-time streaming and processing applications.
Note that this type of stream processing can exist done on the wing based on some predefined events. Additionally, but like messaging systems, Kafka has a storage mechanism comprised of highly tolerant clusters, which are replicated and highly distributed. Past replication, nosotros mean that data can be spread across multiple unlike clusters, minimizing information loss throughout the entire chain.
Kafka can be incorporated into other systems as a standalone plugin. In this example, it tin independently scale based on need. This means that nosotros can scale producers and consumers independently, without causing any side effects for the entire application.
We've seen that edifice a data pipeline involves moving data from a source bespeak, where it is generated to a destination indicate, where information technology is needed or consumed by another application. The source indicate tin can too refer to data output from another awarding,
The lawmaking for this tutorial is bachelor on this GitHub repo. To get a feel of the design philosophy used for Kafka, yous can check this section of the documentation. In a time to come tutorial, we can expect at other tools made bachelor via the Kafka API, like Kafka streams and Kafka connect. For an introduction, yous can check this section of the documentation.
Hopefully, you're at present ready to explore more complex use cases. If you accept any questions, don't hesitate to engage me in the comment section below or hit me up on Twitter.
200's just  Monitor failed and deadening network requests in product
Monitor failed and deadening network requests in product
Deploying a Node-based web app or website is the easy part. Making sure your Node instance continues to serve resource to your app is where things get tougher. If you're interested in ensuring requests to the backend or third party services are successful, endeavor LogRocket.  https://logrocket.com/signup/
https://logrocket.com/signup/
LogRocket is like a DVR for web and mobile apps, recording literally everything that happens while a user interacts with your app. Instead of guessing why problems happen, you can aggregate and study on problematic network requests to rapidly sympathize the root cause.
LogRocket instruments your app to record baseline performance timings such every bit page load time, fourth dimension to starting time byte, slow network requests, and besides logs Redux, NgRx, and Vuex actions/land. Beginning monitoring for gratis.
thompsonwhory1960.blogspot.com
Source: https://blog.logrocket.com/apache-kafka-real-time-data-streaming-app/
Publicar un comentario for "Hpw to Read Data From a File in Kafka Streams"